TYPES OF TINNITUS
WHICH TYPE DO I HAVE?

I HEAR TINNITUS IN BOTH EARS.
MY TINNITUS IS ONLY IN ONE EAR.
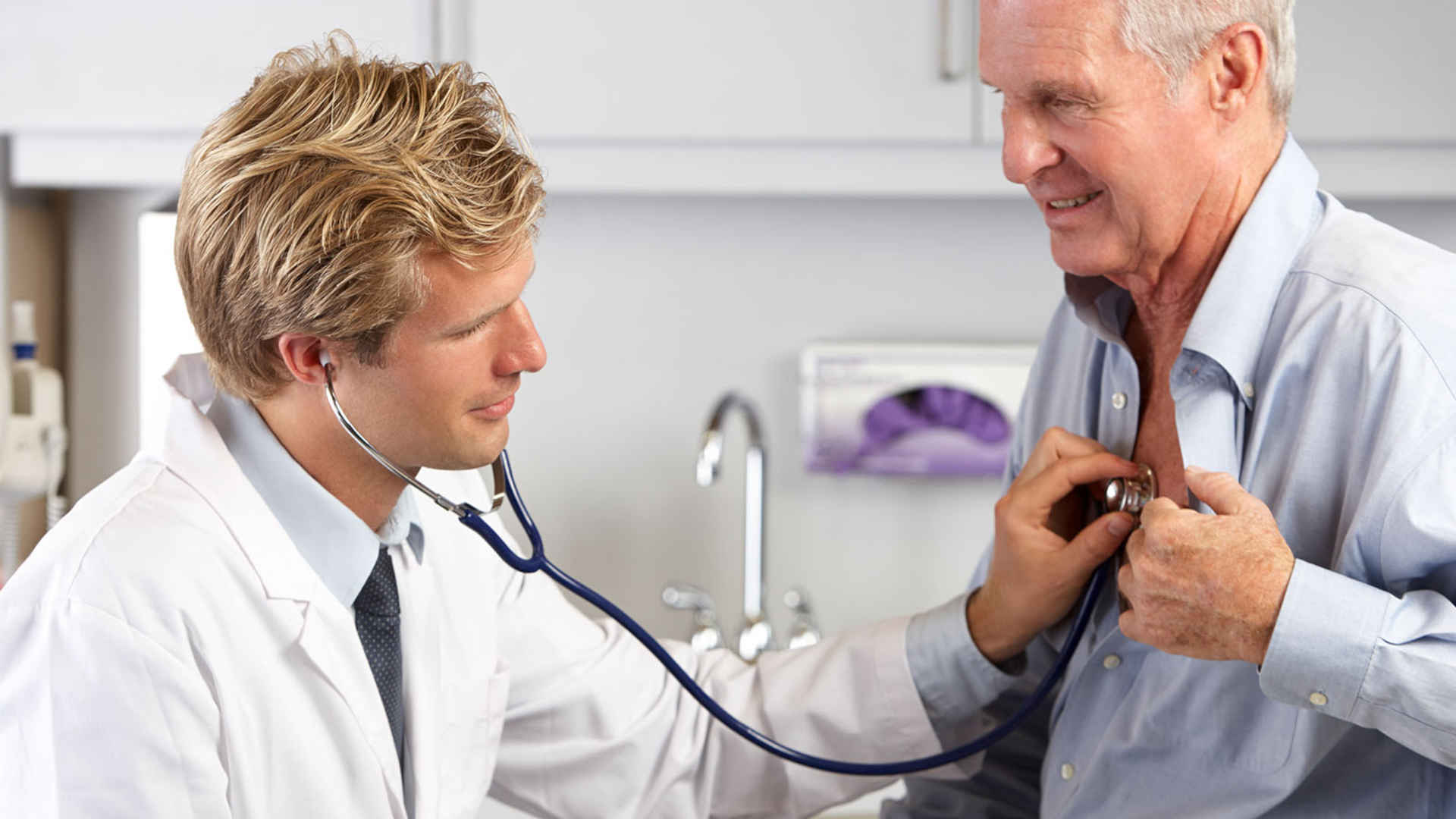
This is called UNILATERAL TINNITUS, which is more rare than bilateral tinnitus. In the case of unilateral tinnitus, the cause can be one that doesn’t automatically affect the whole body or both sides, e.g. a build-up of ear wax in one ear, middle ear infection in one ear, or trauma to one ear or side of the head.
In some cases, unilateral tinnitus can be a sign of a more serious medical condition, therefore we recommend that you seek medical attention from a qualified ear-, nose- and throat-specialist (ENT specialist).


I FEEL LIKE I’M HEARING MY HEARTBEAT IN MY EARS.
Tinnitus that has a rhythmic pattern, e.g. thumping, throbbing or whooshing on a beat, is known as PULSATILE TINNITUS. It has been described a little like hearing your heartbeat in your ears. This type of tinnitus is rarer. Depending on the cause of the pulsatile tinnitus (e.g. vascular disorders), treating the underlying condition may result in eradication of the tinnitus.
In some cases, pulsatile tinnitus can be a sign of a more serious medical condition, therefore we recommend that you seek medical attention from a qualified ear-, nose- and throat-specialist (ENT specialist).
FAQs
Tinnitus in one ear (unilateral tinnitus) can be caused by a variety of factors, including ear infections, build-up of ear wax, or head or neck injuries, amongst others. Unilateral tinnitus is often caused by something that doesn’t ‘automatically’ affect both ears, e.g. build-up of wax in only one ear is possible.